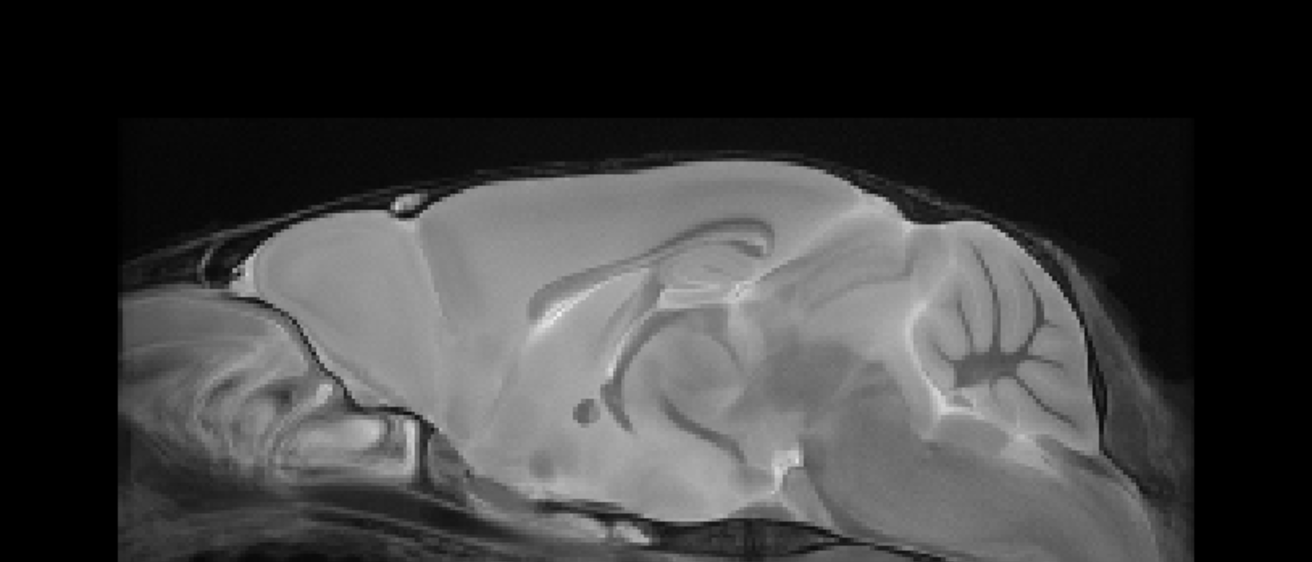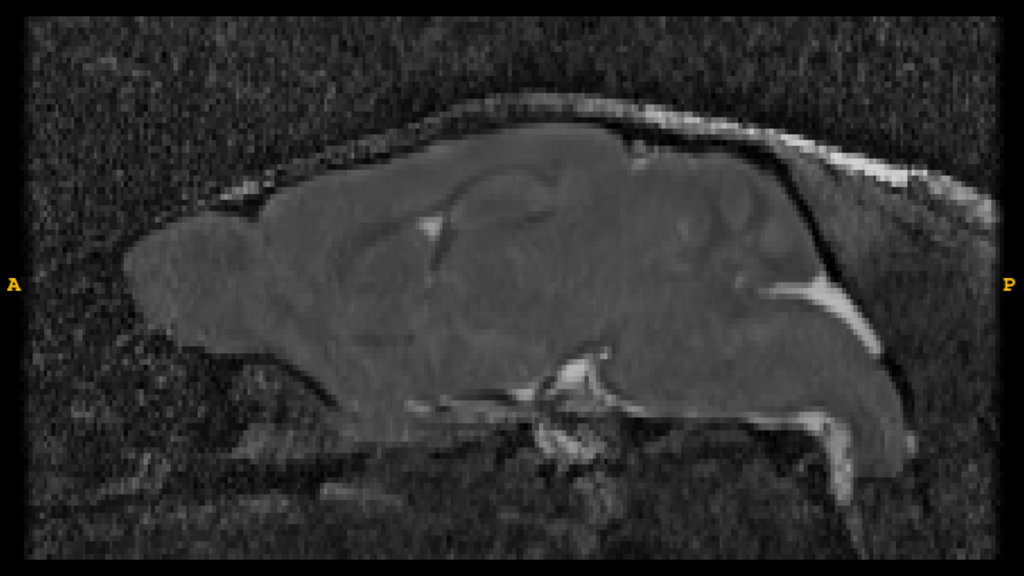
Aquisitions
Here are four examples of our small animal image processing capabilities. See the captions for where to find more information about each method in the drop-down menus below.
T2-Weighted Image
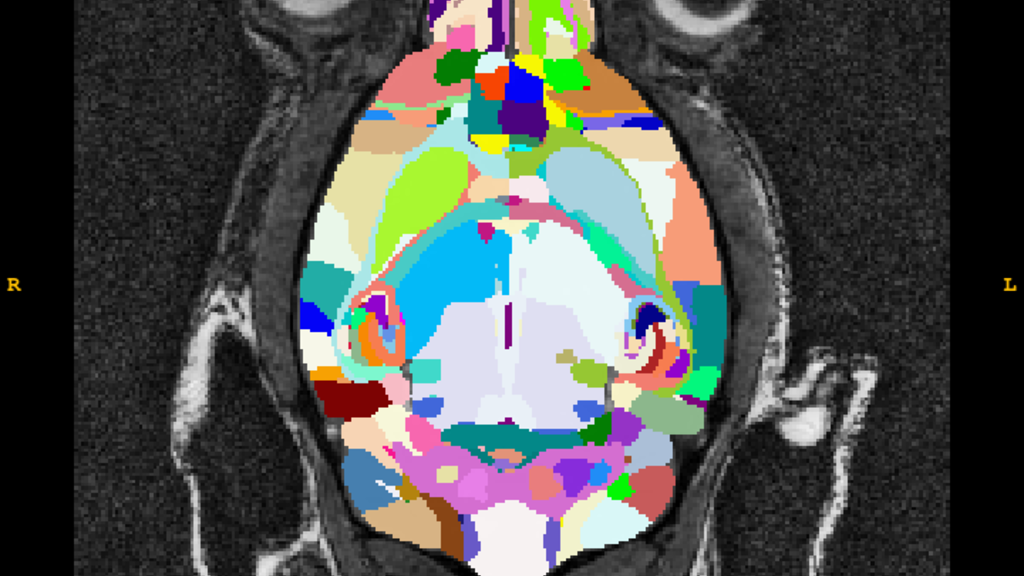
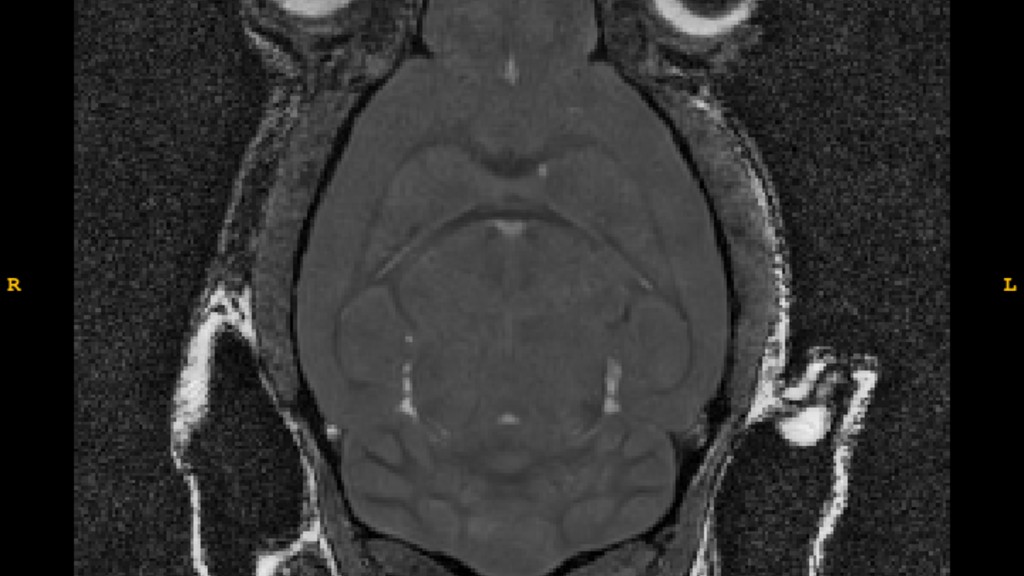
DSURQE Whole Brain Atlas

T2*-Weighted Image
rsFMRI
Anatomical Labeling
DSURQE Whole Brain Atlas
The DSURQE process involves:
- Normalization of native mouse brains to the DSURQE 70um template
- A whole brain T2 weighted high resolution average image of 40 postmortem c57 mice
- Each image is expertly labeled using a modified version of that outlined in the Dorr [1] paper with input from the following papers [2-6] as well (hence, "D-S-U-R-Q-E")
Anatomical Pipelines
INC Anatomical Pipeline
The INC standard anatomical processing pipeline includes:
- Reorientation
- Affining alignment to common space
- Brain extraction
- Denoising
- Intensity scaling and bias correction
- Normalization to standard space(s)
Brain extraction includes:
- A mix of automated methods
- RATS-MM
- BET
- 3dSkullStrip
- Often also requires manual intervention which may increase the processing time and expense
Functional Pipelines
INC Resting-State Pipeline
This pipeline includes:
- Reorientation
- Increasing voxel sizes by some scaling factor
- Fslchpixdim, Rician denoising, N4 bias field correction, rigid/affine/nonlinear motion correction
- Brain extraction
- Registration to standard space
- Calculation of white matter and CSF signals
- Nuisance regression of appropriate regressors (e.g., motion, anatomical, etc)
The process involves:
- Overlaying label sets like DSURQE on the functional data
- The extraction of the timeseries of each label
- The creation of whole brain connectivity matrices
Voxelwise Maps
T2*
T2* image processing provides:
- Estimated values by weighting and combining multiple acquisitions varying in echo time (TE)
It involves:
- Coregistering to each participant/session native space
- Normalizing to template space
References
DSURQE Citations
[1] A.E. Dorr, J.P. Lerch, S. Spring, N. Kabani and R.M. Henkelman "High resolution three dimensional brain atlas using an average magnetic resonance image of 40 adult C57Bl/6j mice", NeuroImage 42(1):60-69, 2008.
[2] Steadman PE, Ellegood J, Szulc KU, Turnbull DH, Joyner AL, Henkelman RM, Lerch JP. Genetic effects on cerebellar structure across mouse models of autism using a magnetic resonance imaging atlas. Autism Res. 2014 Feb;7(1):124-37. doi: 10.1002/aur.1344. Epub 2013 Oct 22. PMID: 24151012; PMCID: PMC4418792.
[3] Ullmann JF, Watson C, Janke AL, Kurniawan ND, Reutens DC. A segmentation protocol and MRI atlas of the C57BL/6J mouse neocortex. Neuroimage. 2013 Sep;78:196-203. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.04.008. Epub 2013 Apr 12. PMID: 23587687.
[4] Richards K, Watson C, Buckley RF, Kurniawan ND, Yang Z, Keller MD, Beare R, Bartlett PF, Egan GF, Galloway GJ, Paxinos G, Petrou S, Reutens DC. Segmentation of the mouse hippocampal formation in magnetic resonance images. Neuroimage. 2011 Oct 1;58(3):732-40. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.06.025. Epub 2011 Jun 17. PMID: 21704710.
[5] Qiu LR, Fernandes DJ, Szulc-Lerch KU, Dazai J, Nieman BJ, Turnbull DH, Foster JA, Palmert MR, Lerch JP. Mouse MRI shows brain areas relatively larger in males emerge before those larger in females. Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 5;9(1):2615. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04921-2. PMID: 29976930; PMCID: PMC6033927.
[6] Beera KG, Li YQ, Dazai J, Stewart J, Egan S, Ahmed M, Wong CS, Jaffray DA, Nieman BJ. Altered brain morphology after focal radiation reveals impact of off-target effects: implications for white matter development and neurogenesis. Neuro Oncol. 2018 May 18;20(6):788-798. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/nox211. PMID: 29228390; PMCID: PMC5961122.
INC DIFFUSION PIPELINE TBD